Readers are invited to download Abaris’ latest engineering and technical presentation, Structural repair methodology for wind turbine blades. Related course descriptions include:
- Composite Windblade Repair course description & schedule
- Structural Engineering for Composite Repair course description & schedule
The abstract from the Structural repair methodology paper is here:
The repair of wind turbine blades is a physically difficult and challenging task. The repair installation team is required to be suspended from a gantry and work on the blade (damage removal and patch installation) in a difficult position. With a well-designed repair scheme its fabrication and installation can lead to more effective implementation.
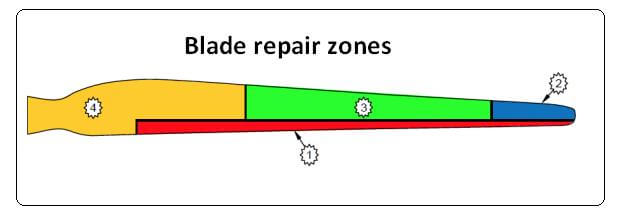
Before a repair, a tech should know the function of each blade zone or section. Zone 1 is the leading edge and Zone 2 is for aerodynamic and aeroelastic purposes. Zone 3 is primarily for aeroelastic functions, and Zone 4 provides torsional rigidity.
An improved wind turbine blade structural repair method is proposed in this paper. Most repair schemes are isolated to surface damage, thus zoning the surface profile of the blade is highly recommended. Specific repair schemes are thus assigned to that zone. Simpler repairs can be achieved through the zoning approach. The zoning of the blade surface profile is based on either, or a combination of, weight, strength, aerodynamic and aeroelastic considerations. A set of recommended repair schemes are also provided in the paper.
Register and download the rest here: http://goo.gl/SIe020
Filed Under: Blades, News




