The requirements for pitch and yaw brakes include high reliability, long maintenance cycles, resistance to environmental influences, and a tight braking-torque tolerance. For pitch drives, one brake manufacturer has developed spring loaded devices as holding brakes that have to perform in a particular way in emergencies, even after a failure. The brake casing is encapsulated.…
No wear surfaces on this brake
MagnaShear motor brakes work by shearing oil for longer service life even in demanding applications. Compressing a fluid shears its molecules– thus imparting torque to a stationary side. The brake eliminates the wear of friction surfaces. A fluid recirculator dissipates heat, a common problem in dry braking systems. Eliminating wear significantly increases service life and…
Braking ideas for wind turbines
David Brooksbank/Altra Industrial Motion. South Beloit, Ill./altramotion.com Brakes for wind turbines call for higher cycles rates, higher loads, greater reliability and often in more compact packages than those on conventional factory equipment. Slowing and halting an 80-m wind-turbine rotor involves converting its kinetic energy into heat. The same mechanical transfer occurs, for example, when stopping…
Yaw brakes for wind turbines
A full array of caliper designs is available from Twiflex, Ltd. to meet the yaw braking-force requirements of any size wind turbine. All brake models are durable, hydraulically activated, and direct applied. Models T20 and T40 deliver up to 40 kN braking force, feature two-bolt side mounting, and are intended for light to medium-duty applications.…
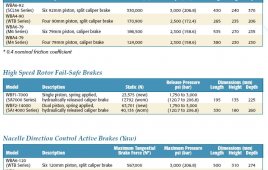
Rotor brakes for wind turbines
Twiflex brakes are fully assembled, provide high levels of reliability, easy electronic monitoring and maintenance, and come with organic or metallic linings. Friction liners are sized to ensure adequate heat dissipation during an emergency stop and with an even pressure distribution across pad surfaces. The brakes come in a range of braking forces from 100…
Soft brake for turbines
Before engineers access a nacelle and hub for maintenance, the rotor must be stopped and secured in a particular position. Today, an electrohydraulic brake control can provide a soft stop to the required position. Then hydraulic controls can engage a rotor lock. Stopping a turbine by the drive train brake alone puts high torque on…
New, longer lasting brake pads for wind turbine
Tribco Inc. will exhibit brake pads that last 3 to 5 times longer than conventional brake pads—but won’t scratch or wear down brake rotors—because they are lined with Braketex, the world’s first and only 100% Kevlar fibered composite friction lining. Braketex is also virtually dust free whereas conventional linings generate dirty, abrasive black dust that…
How to build a better brake pad
The Carlisle Design and Development Process combines the consulting, engineering, modeling, prototyping, testing, and manufacturing required to produce world class brakes. Benefits of the company best design practices lead to: • Complete brake systems – hydraulic controls, brakes, and friction material • Smooth, quiet and reliable braking • Manufacturing and engineering support in US, Europe,…
Brakes for pitch and yaw drives
Emergency braking requirements of today’s large wind turbines under maximum wind conditions are comparable to those of a 40-ton mining truck driving down a 25% grade at 87 mph with a cliff just ahead. To meet these demanding requirements, Warner Electric , South Beloit, Wisc., an Altra Industrial Motion company, modified its ERS series of…