Flashing warning lights on turbine nacelles are mostly for the benefit of aircraft flying at night. The lights have progressed from incandescent to LEDbased units. The features of several recent lights show advanced systems.
One model of obstruction light comes in a one-piece mount. An internal enclosure houses the flash circuitry and GPS synchronization circuitry, so it can synch up with other lights of the same model in the vicinity. A bird spike on the dome discourages its use as a resting pad. The light’s beam projects 360° with a 3° divergence at 50% peak vertical. The 33-lb light comes with a regulated power supply with over-voltage protection, and contacts for monitoring and alarms. An internal photocell eliminates need for an external one, and it runs on 100 to 240 Vac.
Another light features a compact flash head to reduce wind load on fixed obstructions such as wind turbines, towers, and bridges. Operating at just 20W, the series of lights is said to offer the lowest power consumption of any L-864 product (FAA designation for a flashing red obstruction light, 20 to 40 flashes per minute) to help save energy and reduce operating costs. With less than an 8.5-in. height, the shock and vibration-resistant lights offer a low profile to reduce the impact of wind shear on the mounting structure, making it well-suited for high-altitude applications and improved performance in inclement weather.
Another version of obstruction light can be set to a steady burn, or outfitted with a controller for 20 to 40 flashes/min. This LED-based light features optics to minimize ground scatter and nearly eliminate communitylight pollution. In addition, a sharp beam cutoff provides a lower level of scatter—below 0.1 milli-foot candles—over a mile, while delivering an FAA required 2,000 candelas to passing aircraft. Intended to easily retrofit existing incandescent fixtures, the lights offers up to 10 or more years of life expectancy to reduce maintenance costs and frequency of risky tower climbs associated with outdated beacon equipment.
Met towers also need lights. One model aimed at the task comes in a package with equipment needed for FAA approved, solar-powered lighting. The lights are also ETL certified. Packages are available for met towers less than 150 ft. and those over. The L864 red LED beacon runs on 24 or 48 Vdc so it uses 97% less energy than incandescent fixture (only 12W/flash and 24W steady) making conduit unnecessary for most installations. When grid power is unavailable, power can come from a PV panel. Its size is based on load and the available sunlight at the location. Readers interested in more information on obstruction marking and lighting can refer to FAA Advisory Circular AC 70/7460-1K.
While obstruction lights are mostly for the benefit of aircraft, a related observation come from an avian expert familiar with bird migration behavior. She observed that when obstruction lights on wind farms flash out of sequence with each other, migrating birds know enough to fly around the grouping. But when held steady, birds seem to think they are seeing something large on which to land.
Filed Under: Obstruction lighting



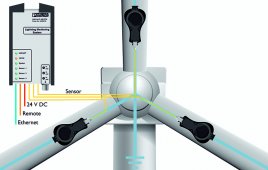

These lights should be build such that there is no light visible from the nearby grounds.
See my Dutch blog for an example solution