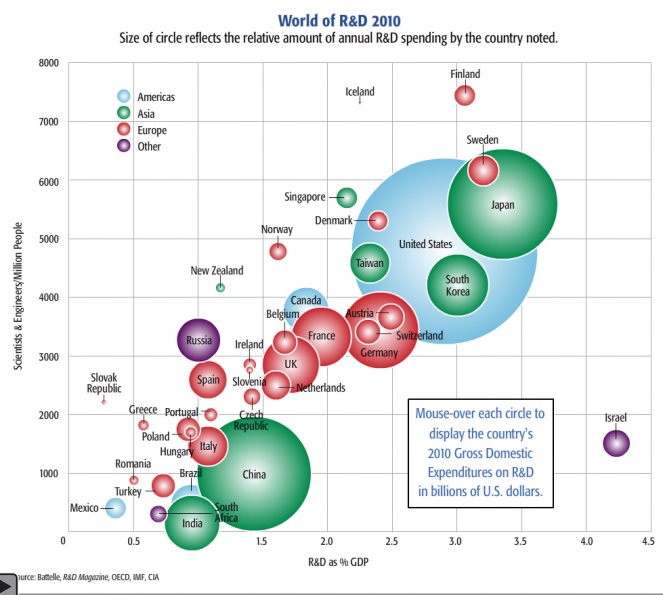
Global research and development (R&D) spending is expected to increase by 3.6% in 2011 to $1.2 trillion, according to the closely watched Battelle-R&D Magazine 2011 Global R&D Forecast.
The forecast predicts that United States R&D will grow by only 2.4% over the final 2010 estimate, reaching $405.3 billion in 2011. With the 2011 inflation rate predicted to remain a low 1.5%, this growth still leads to 0.86%, or $3.4 billion, growth in real terms.
A snapshot of the report reveals the following megatrends:
Globalization increasingly is narrowing the R&D gap between countries.
The U.S. still leads all countries by funding one-third of global R&D.
China has overtaken Japan as the second highest funder of global R&D.
Asia’s stake in R&D spending continues to increase, a shift begun more than five years ago. The U.S., however, still dominates absolute spending at a level well above its share of global Gross Domestic Product.
During the recession of the past few years, the Asian R&D communities generally, and China specifically, increased R&D investment and stature. China entered the recession with a decade of strong economic growth. During that time, it increased R&D spending roughly 10% each year-a pace it maintained during the 2008-2009 recession. This sustained commitment set China apart from many other nations.
“The continued expansion of R&D in China is both inspiring in magnitude and worrisome from a U.S. competitive perspective,” said Marty Grueber, Battelle Research Leader and co-author of the report. “The Chinese are doing everything in their power to grow and develop through an increasing understanding and emphasis on research and technology. Even most of their highest ranking political leaders are engineers.”
The report also includes in-depth looks at R&D activity for specific industries including:
Life Sciences
Information Technologies
Electronics/Computers
Aerospace/Defense/Security
Energy
Advanced Materials
Industrial Outlook: Industry R&D spending in the U.S. will reach $286.9 billion in 2011, a 3% increase of $8.4 billion over 2010 levels. At this level, industrial R&D activities will account for 70.8% of all R&D performed in the U.S.
Federal Government Outlook: Federally performed R&D is expected to decline by slightly more than $200 million, to $27.5 billion in 2011. Part of this decrease reflects the fact that most intramural American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) funds were spent in 2009 and 2010.
Academia: Research by U.S. academic institutions is forecast to reach $57.5 billion in 2011, an increase of 1.9% over 2010.
Global Outlook: While U.S. R&D still dominates worldwide spending, globalization is slowly altering the dominance that the U.S. has maintained for the past 40 years. The economies of China, Korea, India, Russia, and Brazil and their investments in R&D are expanding at rates substantially higher than that of the U.S., Japan, and Germany. As a result, emerging economies are starting to challenge the technological and discovery capabilities of the historic R&D leaders.
Industrial R&D Sector Outlook:
Life Sciences: Merger and acquisition activity has abated somewhat, but it continues to be a defining factor in R&D investment in the pharma, biotech and medical device markets. Post-merger activities, which include cutting, restructuring and streamlining overall R&D costs, will add to the number of pharmaceutical jobs lost over the last five years. The most significant and continuing R&D trend in pharma and biotech is the increasing expansion of R&D efforts in Asia.
Information Technologies: The software industry’s spending on R&D slowed during the recent recession but is projected to see increases in 2010 and 2011. The increase is driven, in part, by the increased adoption of embedded control and interface software in a wide range of applications. Sectors increasingly relying on more software to simulate, design, operate and control products, systems and manufacturing procedures include the telecom, automotive, energy, pharmaceutical, banking and finance, and aerospace and defense industries.
Electronics/Computers: Current hardware technology development is responding to growth in a number of areas including cloud computing, Internet servers, mobile computing, wireless, integrated power supplies, satellite-based communications, flexible circuits and displays, multiple-core processors, carbon nanotube circuits, printed circuits and more.
Aerospace/Defense/Security: No segment has a stronger connection to public R&D investment than aerospace, defense, and national security. In the past, defense budgets have been minimally affected during periods of budgetary constraints, but this is about to change. Many factors are aligning to change the level and focus of defense spending in the future, including significant budget deficits, the growing federal debt crisis and related scrutiny of discretionary spending like R&D, the sluggish economy, the changing status of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars, and the evolving nature of U.S. defense activities in general.
Energy: Outcomes and benefits from federal energy research are realized largely in the private sector. The private sector, however, lacks the full scope of resources to do the research necessary to address growing demand and requirements for sustainability and affordability across all dimensions of energy technology. The government lacks the means to deploy energy innovation at a large scale to achieve policy goals and public benefits. Collaboration and commercialization continue to be the essential bridges. Energy distribution, efficiency, and control technologies in the broad category of “smart grid” are areas of strong R&D interest to a number of key global multinational firms and emerging growth companies.
Advanced Materials: Across all industries, including automotive, aerospace, oil and gas exploration and consumer packaging, there is a common need for lighter, more efficient systems that reduce energy consumption while delivering on the intended mission. Nowhere is materials research more strong in 2010 and 2011 than in nanotechnology.
The full report is available online and interactive graphics are available.
Filed Under: Policy