Availon’s line reactor is less prone to overheating than traditional models. It has special brackets with slots positioned to optimize airflow through the converter cabinet.
The power converter is one of the most sophisticated parts of a modern megawatt-class wind turbine. Its job is to efficiently manipulate the asynchronous power generated by the wind and synchronize it to the correct magnitude, frequency, and phase required by the electric grid. However, manipulating power on a megawatt scale creates a lot of heat, requiring cooling systems to keep critical power electronics cool enough to work efficiently. In warmer climates, ambient temperatures around converter cabinets frequently reach upwards of 130ºF which can shorten electrical component lives. Heat is without a doubt the primary cause of failure for power converter components. Staying on top of regular maintenance and equipment upgrades help avoid excessive downtime, production losses, and overall repair costs.
When components run 20ºC above their maximum rated operating temperature for extended periods, it is not uncommon to see a decrease in component life, as much as 50%. Another way to combat overheating is with upgraded insulated gate bipolar transistors, or IGBTs. These transistors have an increased heat tolerance, good for harsh environments and extending component life, which improves the reliability of the power converter. Additionally, advances in line reactors, such as optimizing airflow through their cabinets, results in greater heat dissipation and enhanced reliability. Availon, for example, offers a line reactor with a 450 A rating for extreme heat conditions.
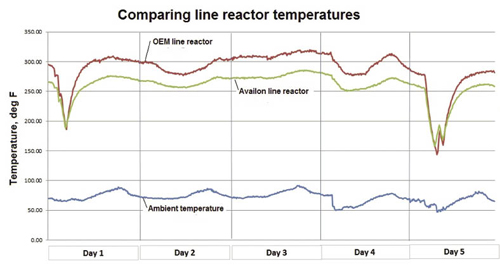
The graph shows temperatures from two adjacent turbines running continuously for about four days with a consistent 20ºC differential in favor of the new line reactor design. The big spikes downward represent the times when the turbine is shut off or not producing power.
Conducting regular maintenance is the best defense for mitigating power converter-component failures. A detailed program helps the cooling system reach its optimal performance and assists in reducing heat damage and failures. Proper converter maintenance should include:
- Frequently checking coolant levels.
- The coolant should be free of particulates. Also verify
that the coolant’s dilution ratio is within
manufacturer’s specifications. - Check for coolant leaks and repair them.
- Verify that the coolant pump is functioning properly.
- All fans should be operational with thermostats set to recommended settings.
- Clean or promptly replace all cabinet filters.
- Heat exchangers should be free of excess dirt and dust.
Filed Under: Featured, Turbines





