If wind turbines are to be built larger, their designers will have to think differently about building larger components. An inventor in Dallas wants to assist with a recent design for a pitch drive could take weight off a rotor and a turbine’s main bearing.
The CAD illustration is from an animation of Hoefken’s mechanism. To view the animation, dial into www.tinyurl.com/macrolever.
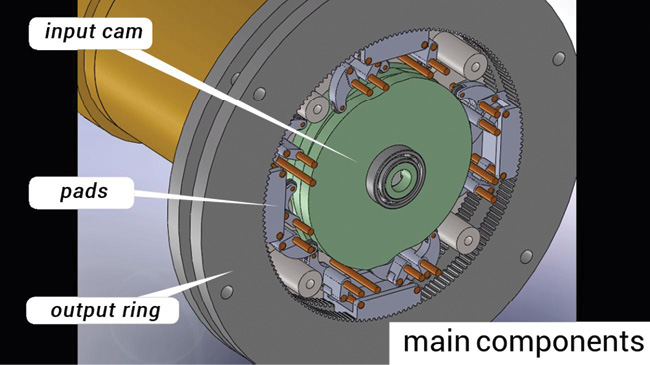
The clever cam-activated mechanism turns a ring gear by “walking” or pulling on four geared pads engaged with the gear. “Torque transmits from a center cam to the pads, while the pads that are stationary for a moment support the output ring by surface contact,” says inventor and designer Carlos Hoefken, founder and CEO of MacroLever Inc. “The pads move in pairs, triplets, or more, so the design generates pure torque. You can think of each pad as a drive.”
The significant feature of the design is that it combines the function of bearing and drive into a single package. Only two pads are lifted and repositioned at a time so the driven gear is supported by the other pads.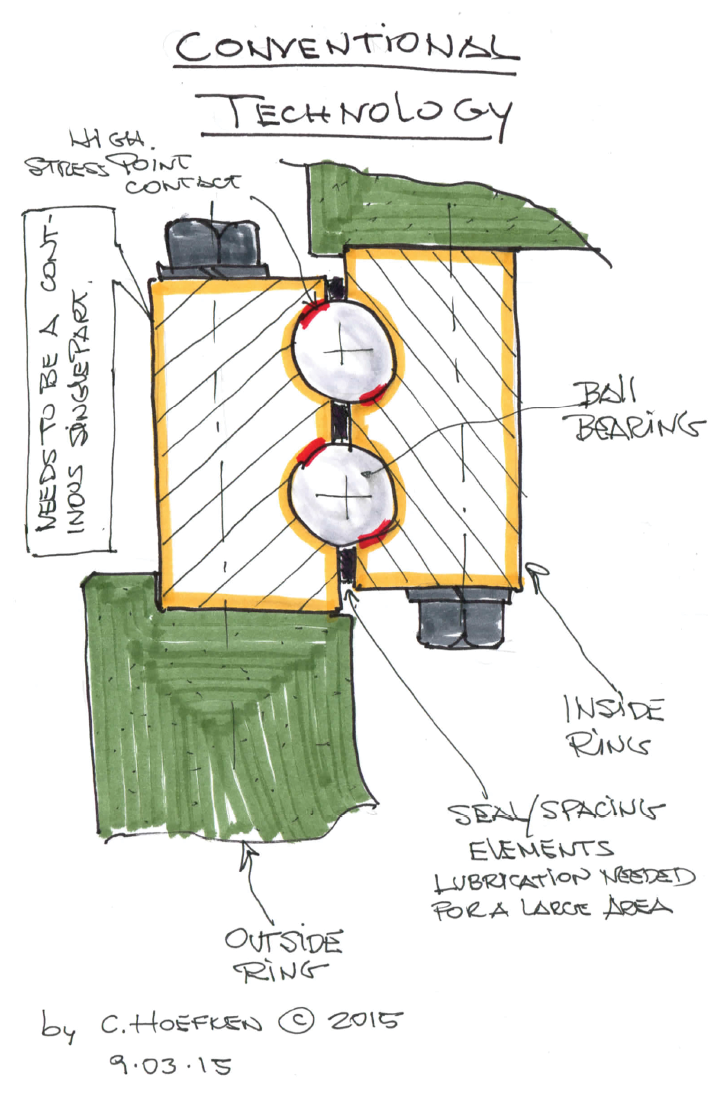
The gear pads hold several mating gear teeth providing a large area of contact unlike a conventional drive which has less than two gear teeth in contact at any one time. Hoefken says his design would weigh only 10% of the gearbox usually selected for a pitch application and would also work without teeth, just a plain surface. “The design could have a ratio a low as 50:1 or as high as 1,000:1 and more,” he says. Other pluses, he says include low maintenance costs, simple lubrication, and a reduced need for costly alloys.
“The main purpose of this invention is to create an electrical alternative to hydraulic drives. For that, the gearboxes must be light and deliver high torques at low rpm and with zero backlash,” says Hoefken.
“I believe this solution will be so economical that it will be possible to add an extra degree of freedom, say elevation angle to a turbine,” says Hoefken. “The elevation angle could deal with wind flows that are not parallel to the horizon which would add a little extra production to wind turbines.”
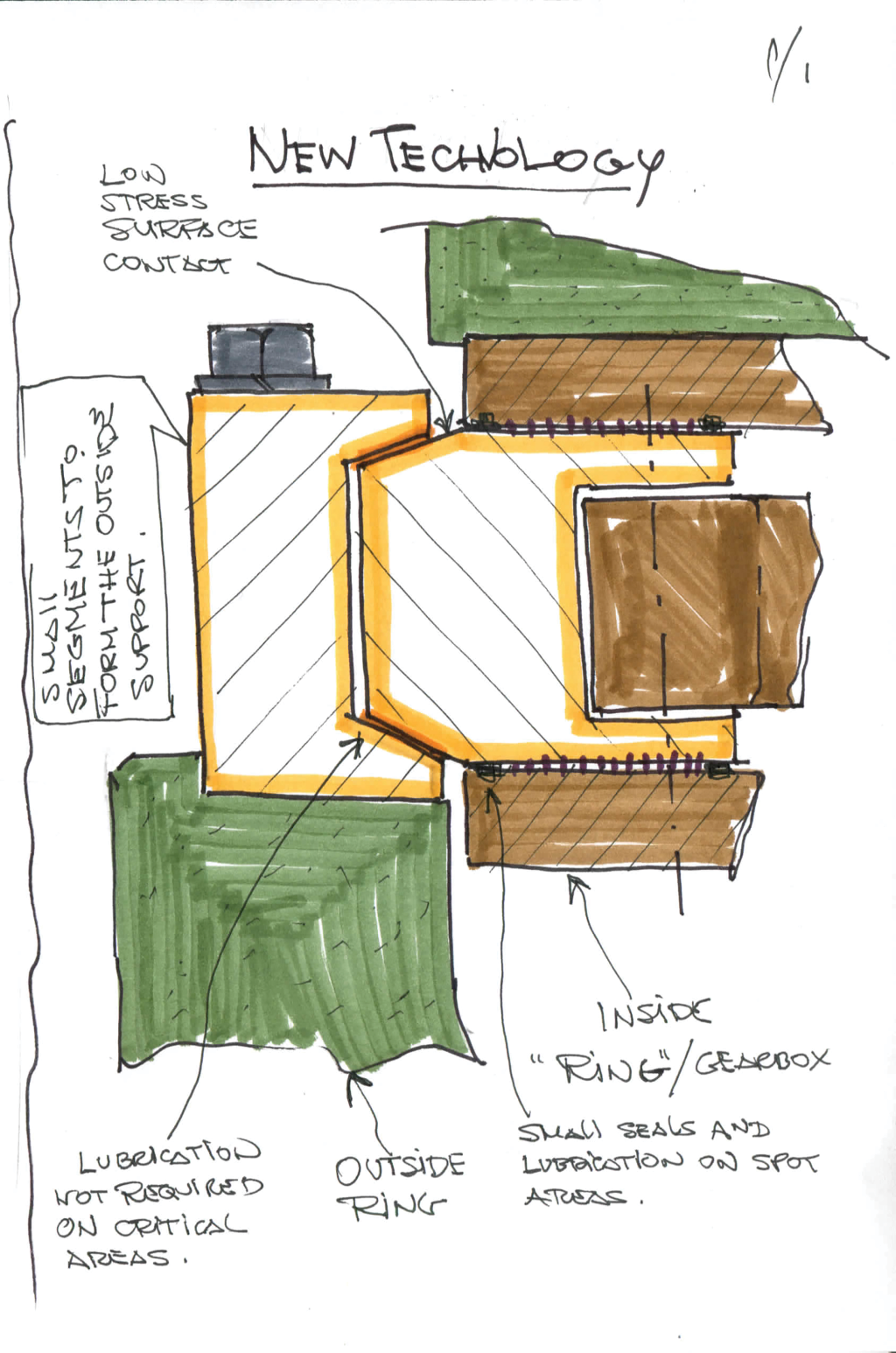 He also sees an application in yaw drives. (See the sketechs on the previous pages.) Designers for large turbines, 3 MW and up, often use up to eight yaw motors and drives to keep the turbine properly oriented. With the new technology, says Hoefken, one drive would be enough to actuate the yaw function.
He also sees an application in yaw drives. (See the sketechs on the previous pages.) Designers for large turbines, 3 MW and up, often use up to eight yaw motors and drives to keep the turbine properly oriented. With the new technology, says Hoefken, one drive would be enough to actuate the yaw function.
“I think we could get rid of several yaw drives in a turbine and use as few as one of these designs,” he says. Yaw functions would be further simplified by omitting the large and expensive three and four-meter diameter yaw bearings. “A substitute mechanism of the type describe here could be made of cast and machined gear segments, which would be much less expensive than a conventional design,” he says.
Hoefken developed the cam operated speed reducer after solving many other motion control issues in industial automation and custom machinery.
Two prototypes of a first and second generation design are working in Hoefken’s Dallas lab. The inventor adds that there are other applications most are which are to replace hydraulic actuators with simpler electric drives. Hoefken says he is already working on a third generation of the drive.
Filed Under: Bearings, Components, Gearboxes, News





I don’t understand very well the concepts (and I am mechanical enginner), maybe i’m not time enough to learn.
but I think this capacity to have other orientation of the horizontal axis, will improve the efficiency of the global production of electrical energy by winds way
can this be usd fro low wind micro turbine say 750 watts orwards
Is it availablle in India